International Journal of General Studies (IJGS), Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2024 https://klamidas.com/ijgs-v4n1-2024-01/ |
|||||||||||
|
The Perceived Impact of Management Styles on the Profitability of Small and Medium-Scale Enterprises in Enugu State By Anthonia Onyinye Ilodigwe
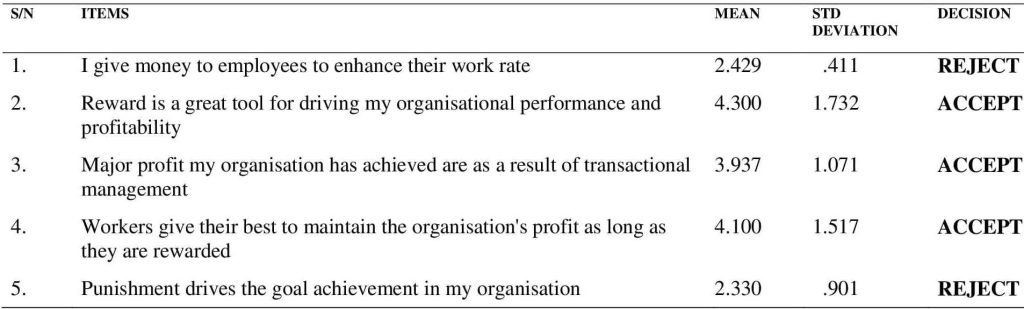
ABSTRACT The activities of Small and Medium-Scale Enterprises (SMEs) have been a subject of continual interest to researchers as they are major contributors to the growth and development of every country. Thus, this study examined the perceived impact of management styles on the profitability of small and medium-scale enterprises in Enugu State. Management is a key factor for improving the performance, productivity and profitability of any organisation. The objectives of this study are to: examined the perceived impact of transactional management style, assess the perceived impact of transformational management style and ascertain the perceived impact of laissez-faire management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. A survey research was adopted for the study and questionnaire was the major instrument of data collection. Data analysis was done using mean and standard deviation. The study found that transactional management especially rewards have positive impact on the profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. The study also found that transformational management style has positive impact on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. The study further found that laissez-faire management style does not have impact of SMEs profitability in Enugu State. Based on the findings of the study, it was recommended amongst others that in order to stay in the competitive business environment, right managers with high capability, creativity and idea be identified at all levels of SMEs in Enugu State. Keywords: SMEs, Enugu State, management styles, profitability INTRODUCTION The aim of every business is to make profit and gain and management is important for achieving the goals and objectives set by every organisation. Management is crucial in a business organisation for several reasons; it is the duty of managers to provide direction, ensure efficient resource utilisation, promote coordination among different departments, and help in achieving organisational goals. It is worth noting that effective management enhances employee productivity, fosters innovation, and enables an organisation to adapt to changes in the business environment. Additionally, management style plays a key role in decision-making, risk mitigation, and in the maintenance of a positive organisational culture that is essential for the smooth functioning, productivity, profitability and long-term success of a business. Hence, the impact of management style in organisations, especially as it relates to profit-making in SMEs, cannot be overemphasised. BACKGROUND TO THE STUDY Small and Medium-Scale Enterprises (SMEs) are set up to achieve certain goals and objectives, with profit-making being usually the main aim. To meet this target, managers of SMEs make use of administrative strategies to oversee the human and material resources of the organisation. Such directorial approaches constitute what is referred to as management styles. Management styles have been in existence for thousands of years. According to Pindur, Rogers, and Kim (1995), elemental approaches to management go back at least 3000 years before the birth of Christ, a time in which records of business dealings were first recorded by Middle Eastern priests. Also, Monye and Eruteya (2018) opined that management styles became an acceptable practice following the published work on theory Y and theory Z management style. From then, various management styles have played out and are still in use. Management style is not about managerial procedure; it is, rather, the managerial framework put in place by the manager to stimulate the workforce. According to Kamusiime (2018), management styles are the different styles used by a manager to influence employees so that they will strive willingly toward the achievement of organisational goals. Management styles are the vital factor in the achievement of success of any business enterprise. It is the prime prerequisite for the realization of organisational objectives. According to Prasetya and Kato (2011), the prime purpose of management style is to enhance employees’ performance so that the objective of the organisation can be achieved. Lloyd and Aho (2020) defined management style as the ability of a superior to influence the behaviour of subordinates and persuade them to follow a particular course of action in order to achieve set goals in a business enterprise. By implication, management style is a multidimensional construct and an extremely vital criterion that determines organisational profit or loss. There are numerous SMEs in the world today and Nigeria as a country also has its portion of SMEs. The activities of SMEs in the contribution of national development and growth cannot be overemphasized as they are also great employers of labour. In southeastern Nigeria, there are numerous businesses in the category of SMEs that contribute to the growth of the region. Most of the region’s inhabitants are business oriented; this can be attributed to the apprenticeship system (“Igba boy”) that is inherent in the business culture of the region. The importance of management in SMEs’ profitability and general operations made it important that this study is carried out in Enugu State which is a hub for numerous SMEs in contemporary times. STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM Management style determines the level of subordinate participation in decision-making and the way a business enterprise is run administratively. Business enterprises’ performance and profitability can be greatly affected adversely if they have bad managers or managers who find it difficult to adopt a suitable management style. Thus, research has shown that whether a business enterprise is profitable or not depends on how managers conceive and handle the affairs of the business (Michael, 2010). Thus, management style adopted by managers may determine the level of output given by employees in terms of productivity and, invariably, profitability. Good management styles are also important for employees in SMEs because when employees are well managed, they provide quality service and make sure organisational goals and objectives are met (Girlando and Eduljee, 2010). Conversely, when employees are not well managed at their work place, the resultant outcome is poor organisational performance. So, it is important to find out which management style works best for SMEs, especially in Enugu State, the environment of this study and research. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES The broad objective of this study is to investigate the perceived impact of management styles on the profitability of small and medium scale enterprises in Enugu State. Specifically, the study: I. Examined the perceived impact of transactional management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. II. Assessed the perceived impact of transformational management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. III. Ascertained the perceived impact of laissez-faire management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. RESEARCH QUESTIONS Based on the research objectives, the following research questions were asked. I. What is the perceived impact of transactional management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State? II. What is the perceived impact of transformational management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State? III. What is the impact of laissez-faire management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State? LITERATURE REVIEW Management Styles Management style is a managerial term often used to describe the way managers carry out their activities in an organisation. It is a function of behaviour associated with personality (Herrity, 2021). Management style can be understood as a way to manage an organisation. According to Yanney (2014), management style is the adhesive that binds diverse operations and functions together. It is the philosophy or set of principles by which the manager capitalizes on the abilities of the workforce. Management style is not a procedure on how to do but it is the management framework for doing. A management style is a way of life operating throughout the enterprise and permits an executive to rely on the initiative of the personnel of an entity. Types of Management Styles There are several management styles adopted by managers. However, the study focuses on three management styles, as stated in the objectives. These are transactional management style, transformational management style and laissez-faire management style. Transactional Management Style Transactional leadership style is the management style by which managers are able to entice subordinates to perform and thereby achieve desired outcomes by promising rewards and benefits for the accomplishment of tasks and administering punishments when tasks are not well accomplished (Yanney, 2014). Sayadi (2016) indicates that transactional management style consists of contingent reward, active management by exception, and passive management by exception. These authors further show that a transactional manager motivates subordinates by giving rewards for successful services provided. This type of managers clarifies the employees on goals and arranges contingent rewards as inducements toward the achievement of the goals. The transactional management style has been reported to be a market-based exchange process where managers and employees negotiate tasks for different types of rewards (Oyelade, Akpa, Olawore, Adesanya, & James, 2022). The transactional manager forms a mutual agreement with the employee about his or her responsibilities and expectations are kept closely to that agreement. Transactional managers are reward and punishment-oriented (Hoxha, 2019). Transformational Management Style Transformational management style occurs when employees are motivated to meet the highly challenging expectations of the organisation. Transformational managers tend to help employees find new ways to meet organisational challenges (Lin, Xian, Li & Huang, 2020). The most frequently used definition of transformational management refers to a manager’s behaviour, influential traits, power and situational variables that influence employee performance in a positive direction such as motivating employees to work more than expected and enjoy the work they do (Alsalami, Behery & Abdullah, 2014). Transformational management style is a management philosophy that encourages and inspires employees to innovate and develop new ways to grow and improve the path to an organisation’s future success (Khan, Rehmat & Butt, 2020). Using this style of management, managers give trusted employees the independence to make decisions and support new problem-solving approaches. Transformational managers are passionate about their work and the organisation’s mission, while also helping all employees succeed. Another key trait of transformational managers is their ability to identify business processes that no longer work and focus on streamlining or changing them as needed. The transformational leadership approach encourages, inspires, and motivates employees to innovate and create the change necessary to shape the future success of the company. Laissez-faire Management Style “Laissez-faire” means “leave it be” in French. It is used to describe managers who leave their employees to work on their own. Laissez-faire management could be effective if the manager monitors what is being achieved and communicates this back to the team regularly. Laissez-faire management style is a type of management style in which the manager hands-off and allows group members to make the decisions. Employees are empowered to determine their own objectives, solve their own problem and make their own decision with little or no interference. Often, this style of management is most effective when individual employees are very experienced and skilled self-starters. The preference for any of these management styles vary among managers. Some may prefer an autocratic style where they tell employees what to do and how to do it. Others prefer a democratic style where they help their employees to discover solution to problems for themselves. Some believe in laissez-faire management style in which the manager hands off and allows group members to take decision. No matter the kind of management style the manager adopts, the bottom line is that of improving employees’ performance and that of the organisation. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK Both theory X and Y and the principle of scientific management formed the theoretical framework for this study as the theories one way or the other try to explain the way management styles play out in various organisations. Theory X and Y was propounded by American social psychologist Douglas McGregor in his book, The Human Side of Enterprise, where he concluded that two different styles of management are guided by their managers’ perceptions of team member motivations. According to McGregor (1960), there are two opposing perceptions about how people view human behaviour at work and organisational life. Theory X is based on the reward system that drives organisational performance and is mostly related to transactional management style. On the other hand, theory Y focuses on how managers drive organisational performance using other important factors like creativity, teaching, and even ideas of employees. Theory Y is more focused on the transformational management style and laissez-faire management style. The principle of administrative management theory was propounded by Henri Fayol, a senior executive and mining engineer. He developed this theory in the 19th century when he examined an organisation through the perspective of the managers and situations they might encounter. The principle of administrative management theory is the general view of what managers will do in a given situation to drive organisational performance and profitability. METHODOLOGY The area of the study is Enugu State because the state has seen a remarkable rise in the activities of SMEs and in the level of their contribution to the economy of the state. The survey research design was used for the study in order to achieve the study’s objectives. The population of the study is made up of 250 purposively selected SMEs managers from all the Local Government Areas of Enugu State. The instrument of data collection is a structured questionnaire that comprised of close-ended questions made of 5-point Likert scale of Strongly Agreed (A), Agreed (A), Undecided (U), Disagreed (D) and Strongly Disagree (SD). The questionnaire was structured to achieve the research objectives. Pilot test was used to determine the reliability of the questionnaire and the Cronbach Alpha Coefficient of the test yielded 0.83. The instrument was distributed on a face-to-face basis and consent was sought from the respondents. Data collected for this study was processed using SPSS version 25. The nature of data analysis in this research was largely descriptive. Thus, mean rating and standard deviation were used to analyse the data for the study. DATA PRESENTATION AND ANALYSIS Research Question 1: What is the perceived impact of transactional management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State? Table 1: Mean and standard deviation of the impact of transactional management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State
Table 1 shows rejection with mean rating 2.429 and standard deviation of .411 that managers give money to employees to enhance their work rate. The table, on the other hand, shows acceptance with mean rating 4.300 and standard deviation 1.732 that rewards is a great tool for driving SMEs performance and profitability. The table also shows acceptance with mean rating 3.937 and standard deviation of 1.071 that major profits achieved by SMEs are as a result of transactional management. The table further shows acceptance with mean rating 4.100 and standard deviation of 1.517 that as long as workers are rewarded, they give their best to maintain their organisation’s profit. Lastly, the table shows rejection with mean rating of 2.330 and standard deviation value of 0.901 that punishment drives the goal achievement and performance of SMEs. The general finding of table 1 shows that transactional management, involving rewards, has positive impact on the profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. Research Question 2: What is the perceived impact of transformational management style on productivity of SMEs in Enugu State? Table 2: Mean rating and standard deviation of the impact of transformational management style on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State
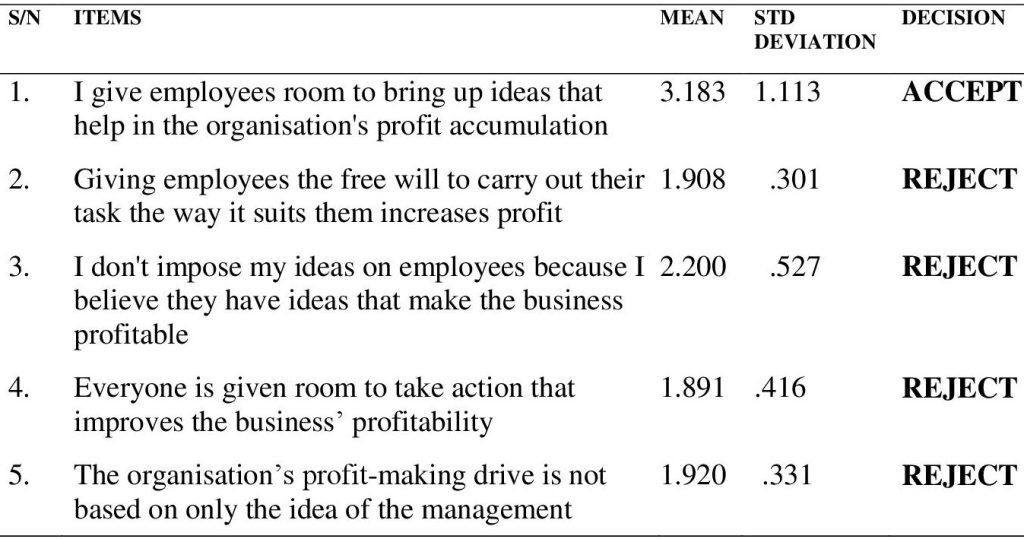
Table 2 shows the mean rating and standard deviation of the perceived impact of transformational management style on the productivity of SMEs in Enugu State. From the data presented in the table, acceptance was shown with mean rating of 3.341 and standard deviation value of 1.132 that manager’s creativity is a driving force of the organisation’s profitability. The table also shows acceptance with mean rating 3.837 and standard deviation value of 1.206 that managers ideas help employees accomplish their daily tasks in the organisation. The table further shows acceptance with mean rating 3.529 and 1.235 that managers intellectual power helps organisation to overcome challenges that hinders profitability. Furthermore, the table shows acceptance with mean rating 3.779 and standard deviation 1.310 that managers are inspiration to employees and their abilities in achieving organisational goal. The table with mean rating 4.466 and standard deviation value of 1.831 also shows acceptance with mean rating that managers motivation is an important factor that keeps organisation in profit. The general findings of table 2 shows that transformational management style has positive impact on profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. Research Question 3: What is the perceived impact of laissez-faire management style on productivity of SMEs in Enugu State? Table 3: Mean rating and standard deviation on the impact of laissez-faire management style on SMEs in Enugu State
Table 3 shows the mean rating and standard deviation on the perceived impact of laissez-faire management style on SMEs’ profitability in Enugu State. From the table, acceptance was shown with mean rating of 3.183 and standard deviation value of 1.113 that employees are given room to bring up ideas that help in SMEs’ profit accumulation. The table on the other hand shows rejection with mean rating of 1.908 and standard deviation value of 0.301 that giving employees the free will to carry out their task the way it suits them increases profit. The table also shows rejection with mean rating of 2.200 and standard deviation value of 0.527 that managers don’t impose their ideas on employees because they believe employees have the ideas that make SMEs profitable. The table further shows rejection with mean rating 1.891 and standard deviation value of 0.416 that managers give room to everyone to take action that improve SMEs’ profitability. Furthermore, the table shows rejection with mean rating 1.920 and standard deviation value of 0.331 that profit-making drive of SMEs is not based on only the idea of the management. The general findings from table 3 shows that laissez-faire management style does not have impact on SMEs’ profitability in Enugu State. CONCLUSION Based on the findings of the study, it is evident that managers of SMEs make use of transactional management style and this, to some extent, impacts on SMEs’ profitability. Transactional management style impacts on the profitability of SMEs especially through the use of rewards as workers give their best when rewarded, and this leads to increase in SMEs’ profitability. The findings of the study also show that transformational management style has impact on the profitability of SMEs in Enugu State. Transformational management style impacts on SMEs’ profitability through the creativity, ideas, intellectual power, inspiration and motivation of managers. This finding proves that the qualification and capacity of managers are important for organisational growth, development and profitability. The study, on the other hand, concludes that laissez-faire management style has little or no impact on SMEs’ profitability in Enugu State. This is as a result of the fact that giving employees the free will to carry out their task the way it suits them does not increase profit. Also, laissez-faire management style is barely used by managers of SMEs as managers impose their ideas on employees because managers believe that employees don’t have what it takes to make SMEs profitable. The study further concludes that although profit-making of SMEs is not based on only the idea of managers, everyone in the organisational setting of SMEs is not given room to take action that improve SMEs’ profitability. This can be as a result of managers wanting to be fully in control of their organisations, thereby making sure that ideas and activities that may hinder their organisation’s profitability are put in check and not carried out. RECOMMENDATIONS Based on the findings of the study it was recommended that:
REFERENCES Alsalami, E. Behery, M. & Abdullah, S. (2014). Transformational Leadership and Its Effects on Organisational Learning and Innovation: Evidence from Dubai. The Journal of Applied Management and Entrepreneurship. 19. 61-81. 10.9774/GLEAF. 3709.2014.oc.00006. Herrity, J. (2021). Management Styles: Overview and Examples | Indeed.com. [online] www.indeed.com. Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/ career-development/ management-styles. Hoxha, A. (2019). Transformational and Transactional Leadership Styles on Employee Performance. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention (IJHSSI), 8(11), 36-48. Kamusiime, B. D. (2018). Management style and employee performance in selected primary schools in Kajaracounty, Ntungamodistrict. A research report submitted to the directorate of postgraduate training for the partial fulfilment for the award of master of arts in education management of Kabale University. Unpublished. Khan, H., Rehmat, M., Butt, T.H. (2020). Impact of transformational leadership on work performance, burnout and social loafing: a mediation model. Futur Bus J 6, 40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00043-8 Lin, C. P., Xian, J., Li B., & Huang, H. (2020) Transformational Leadership and Employees’ Thriving at Work: The Mediating Roles of Challenge-Hindrance Stressors. Front. Psychol. 11:1400. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01400 Lloyd, R. &Aho, W., (2020). “The Four Functions of Management – An essential guide to Management Principles”. Management Open Educational Resources. 1. DOI: 10.58809/CNFS7851 McGregor, D. (1960). The Human Side of Enterprise. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York. Michael. A. (2010). Leadership Style and Organisational Impact. Retrieved from: Morgan, G. (1988). Teaching MBAs Transformational Thinking. In R.E. Quinn & K.S. Cameron (Eds.). Paradox and Transformation: Toward a Theory of Change in Organisation and Management. Cambridge, Ballinger Monye, M.C. & Eruteya, E. (2018). Effect of transportation model on organisational performance: A case study of MTN Nigeria, Asaba Delta state, Nigeria. International Journal of Innovative Social Sciences and Humanities Research, 6(2), 76-82 Oyelade, K. A., Akpa, V. O., Olawore, O.P., Adesanya, A. S. & James, M. T. (2022). Transactional Leadership Style and Market Share of Selected SMEs in Lagos State, Nigeria, Journal of Human Resource & Leadership, 6(2), 57-71. https://doi.org/10.53819/81018102t4059 Pindur, W., Rogers, S.E. and Suk Kim, P. (1995). The history of management: a global perspective. Journal of Management History (Archive), [online] 1(1), pp.59–77. doi:https://doi.org/10.1108/13552529510082831. Prasetya, A. & Kato, M. (2011). The Effect of Financial and Non-Financial Compensation to the Employee Performance. The 2nd International Research Symposium in Service Management. Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Sayadi, Y. (2016). The effect of dimensions of transformational, transactional, and non-leadership on the job satisfaction and organisational commitment of teachers in Iran. Management in Education, 30(2), pp.57–65. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/ 0892020615625363. Yanney, J. (2014) Business Strategy and Leadership Style: Impact on Organisational Performance in the Manufacturing Sector of Ghana. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 4, 767-775. doi: 10.4236/ajibm.2014.412083.
|
|||||||||||