Journal of Education, Humanities, Management and Social Sciences (JEHMSS), Vol. 1, No. 2, June-July 2023. https://klamidas.com/jehmss-v1n2-2023-02/ |
|||||
|
Talent Management and Organizational Performance in Pharmaceutical Companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria
Ifeoma Evangeline Odunukwe & Ifeanyi Victor Okeke
Abstract This work examined the effect of talent management and organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. The study reviewed relevant conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature. This study is anchored on Human Capital Theory. Talent retention, training and development, and talent attraction were employed as the explanatory variables while organizational performance is the dependent variable. The study adopted survey research design. The population of the study comprises the staff of the pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria – 1824. Sample size of 332 respondents was selected for the study using Borg and Gall (1973) formula. Questionnaire was employed as the main instrument of data collection. The data generated were analyzed using frequency, percentage analysis, and multiple regression analysis. The study found that talent retention has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. Training and development has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance and talent attraction has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. The study concludes that talent management has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. The study therefore recommends that management should make retention a priority since an organization’s strength and future success are not only dependent on its financial resources but ultimately depends on effective talent management. Management should not only focus on attracting talented individuals but should do more to retain the most talented among them as it would enhance the growth and sustainability of pharmaceutical companies. Keywords: talent retention, training and development, talent attraction, organizational performance
INTRODUCTION Talent management has almost become an inevitable management function in modern times. Due to tough competition in every sphere of business today, organizations are vying for the best people from the job market. Attracting the best talent from the job market is not everyone’s cup of tea. It requires a lot of competence, expertise and experience on the part of the organization to recruit the best in the industry. Human capital has vital intellectual, economic, and social dimensions, and this is why organizations are paying serious and comprehensive attention to the management of their human resources, developing appropriate strategies aimed at deriving maximum benefits from their human capital investment. This will also help organizations to successfully manage their competitive strategies (Almutairi1 & Alsawalhah, 2020). A major part of the human resource department is devoted to talent management, which is mostly dedicated to the purpose of recognizing, sourcing and poaching best talent. Talent management can be defined as a deliberate approach implemented to recruit or hire, develop and retain people with required aptitude or skills to meet the present and future goals or needs of the organization. It is the creation and maintenance of a supportive and pro-people organizational culture. Talent management is, therefore, the commitment of an organization to recruit, develop, retain the most talented and qualitative employees available in the job market. Talent management starts with identification of the appropriate skilled people required for the organization and then a proper selection of people with requisite potentials and skills in desired job. After identification and selection of the right kind of people, talent management implements competitive compensation that may include attractive pay-package, periodical increment, health insurance, and paid leaves, etc. for the employees. The selected workforce is provided with training and regular refreshment programs so as to match the emerging requirements of the organization. In a study, Bersin (2016) asserts that growth potential of organizations worldwide depends on the ability of organizations to have the right people, in the right place at the right time. Employers are forced to compete to attract and retain an increasing pool of talented individuals in order to achieve their objectives. Companies with effective talent management practices deliver better results for shareholders (Huselid, 2015). Effective talent management practices can create enduring competitive advantage and enhance organizational productivity. Srihandayani and Kusnendi (2018) conducted effect of Talent Management and Organizational Culture on the Performance of Employees (Study on Employee Brantas Abipraya Company, Jakarta). These studies revealed that talent management and organizational culture have significant effect on employee performance. Due to scarcity of talent, organizations around the world are competing for the same pool of talents to acquire and retain talents in order to maintain their operations and continue to grow in terms of service and profitability. Most assets of an organization such as, products, technologies and strategies may be replicated easily but human capital takes great deal of time to develop and considered as a key asset to manage and adapt to the organizational needs (Guthridge, McPherson, & Wolf, 2019). In a globalized era, managing and developing talent has become a crucial factor in the success of an organization. Talent Management is not limited to acquiring the right candidate but, beyond that, it extends to identifying the untapped and unusual qualities of your employees to develop and retain them to get the desired results. Talent Management is defined as ‘the systematic attraction, identification, training and development, engagement/retention and deployment of those individuals with high potential who are of particular value to an organization’. Talent Management has gained more ground and relevance due to the evolution of corporate human resource and training in today’s present work environment. The concept of talent management originated in 1990 when the responsibilities of human resources departments shifted from being mainly routine administration processing to more complex configuration and machine-based planning duties. Decision makers exclusively relied on HR department for employee management and training in the competent evaluation of modern industry and business sectors. Again, HR plays vital role in developing good compensation packages which include: employees’ fringe benefits, stock options and bonuses, and serving as a central point of communication for employee health and happiness (Bersin, 2016). Studying the impact of talent management on organizational performance is based on the assumption that talent management improves organizational performance by attracting and retaining the talented people it needs (Armstrong & Taylor, 2014). The goal is to create a positive and comfortable environment for employees, strive to get employees who are satisfied and then engaging them. It is against this background that this study examines the effect of talent management and organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta area of Nigeria. Statement of the Problem Today, most organizations are struggling to have a clear understanding of the definition and characteristics of talent management and its enabling technologies. Even though they know how to administratively recruit, retain and replace, they are still struggling with the strategic elements of managing talent. However, despite the high cost of developing the pharmaceutical workforce, talented employees in the focused firms appear to be changing jobs into other fields of endeavour. Some pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta attract and hire top talents, train and develop vibrant and sustainable pool of intellectual capabilities yet face the challenge of replacing experienced and talented employees. This is probably because they play down on attracting, training, development and retaining workers. They probably lose some key intellectuals to competitors who offer similar services/products while some opt out to start their own private businesses on a smaller scale. Issues such as grievances, absenteeism, low morale, voluntary resignation, negative attitude to work, pilfering, and high turnover rates of top talents abound. The determinants of talent management in this study include: talent retention, employee training and development and talent attraction The problems of this study focused on the effects of talent retention, employee training and development and talent attraction, as independent variables and organizational performance as dependent variables with special reference on organizational performance. It is against this backdrop that this study seeks to examine the effect of talent management and organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Objectives of the Study The general objective was to examine the effect of talent management and organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. The specific objectives are to:
Research Questions The following were formulated to give this study direction.
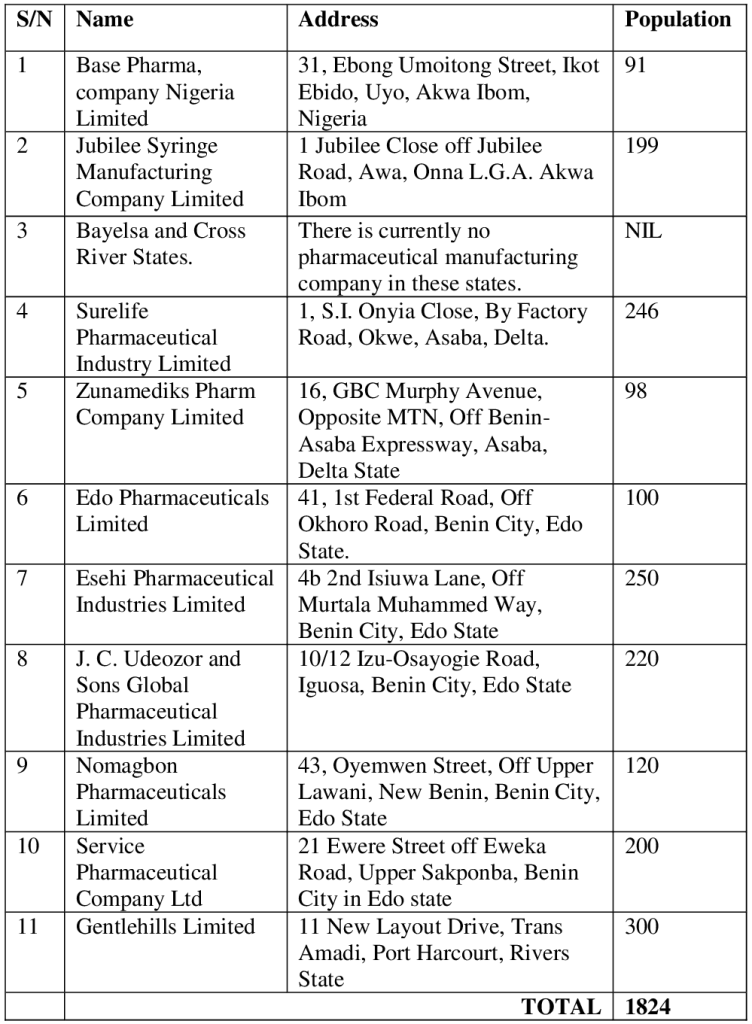
Hypotheses The following null hypotheses were formulated to give direction to this study. Ho1: Talent retention has no positive significant relationship with organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. Ho2: Training and development has no positive significant relationship with organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. Ho3: Talent attraction has no positive significant relationship with organizational pharmaceutical in pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE Conceptual Framework Talent Management The word talent means a factor that differentiates the performance of every employee in an organization or company. If a company wants to increase profits in its current line of business and continue to grow and develop its existing company, the company must focus on finding, attracting, and retaining the best employees. A good company is a company whose vision, mission and company values that have been previously set are carried out by a number of talented employees who work together and synergize (Pella & Afifah, 2017: 70). Employee talent must be managed by the company properly with a good management system. A talent management system that is implemented in an integrated manner and in line with other management functions will provide a real increase in business performance and employee performance. A successful company is one that creates a well-developed talent culture. Employee talent development culture consists of programs that specifically consist of company strategies in selecting the right employees, placing employees according to their abilities and skills, providing training and employee development that can improve performance at work and retain employees by providing compensation (Pella & Afifah, 2017: 75). According to Pamela et al. (2017), results proved that talent management initiatives at Lebanese Banks impacted on the leadership quality, business unit productivity and teamwork in the organization. Eglal Hafez et al. (2017) found that the components of talent management (motivating outstanding performance, training and development, job enrichment) have a significant impact on job satisfaction and on employee retention. Deepika and Sampurna (2018) conclude that a synchronization of talent management practices and employee engagement initiatives leads to improved talent retention and proposes a model to this end. Erkut et al. (2018) found that effective talent management practices have important influences on human resources, which is the most critical element in a company’s survival. Hitu and Satyawan (2018) indicate that talent management practices have direct impact on employee motivation, employee creativity, employee satisfaction and employee competency. Results from Nadine and Abubakr (2019) empirical research uncover that talent management and employee recognition can significantly affect the level of employee performance as well as contributing to organizational success and positioning. This study also found that talent management and employee recognition are interrelated variables that affect employee performance. Syed et al. (2019) results indicated that talent management strategies significantly and positively affect employees’ performance behavior; whereas talent management outputs partially mediate the relationship between talent management strategies and employees’ performance behavior. Outcomes of Munaza (2019) study revealed a significantly positive effect of talent management practices i.e. recruitment and selection for talent attraction, coaching and mentoring for learning and development of talent, compensation for retention of talent on employee performance. Amina and Parbudyal (2020) found that, based on theoretical framework in the context of both inclusive and exclusive talent management, perceived equity is a valuable resource that motivates employees and results in favourable outcomes. Moza et al. (2020) concludes that the three independent variables to talent management practices, i.e recruitment, selection and learning & development, strongly impact organizational performance in Islamic banks in Kenya; but not for employee retention which has no impact on organizational performance. Wickramaaratch and Perera (2020) study revealed that talent management has a significant positive impact over employee performance and job satisfaction and also proposed that adopting talent management is worthwhile as it leads to attracting and retaining a satisfied young generation and improved performance at work. Results of the study by Riham and Tarik (2020) show that talent attraction and talent retention have no impact on sustainable organizational performance whereas learning and development and career management were found to have significantly positive impacts. Hayfaa (2021) study indicated relative consensus in talent philosophies across organizations in four industries; talent was largely perceived as exclusive, despite disagreements on whether it was stable or developable. Differences were identified in terms of how talent management was understood in organizations and also how it was executed in practice in terms of talent identification and recruitment, training and development, performance assessment and talent retention. Oluwatobi and Gabriel (2021) concluded that talent management practices had an effect on job performance of librarians in university libraries in the South-West of Nigeria. Organizational Performance Organizational performance is a way of measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of organization’s action which has to do with the assessment of advancement made towards the attainment of the set objectives. In business it is recognized as a central outcome variable of interest, ranging from human resources and marketing to operations management. Organizational performance encompasses the actual outputs or results realized by an organization, measured against the intended outputs, mainly considered as objectives and goals or the previous period performance (Hailey, 2006). Views posited by Richard et al. (2009) depict organizational performance as comprising of three specific parts of organization outcomes that include product market performance, financial performance and shareholder return. Organizational performance is also defined as a set of financial and non-financial indicators that offer information on the degree of attainment of the organization’s objectives (Jaleha & Machuki, 2018). Most organizations measure their performance based on the effectiveness of achieving company goals, while another significant majority views it in terms of efficiency in deploying resources (MacPherson & Pabari, 2004; Derda & Dea Flores, 2017). High organizational performance is realized when all fragments of an organization work in unison to attain great results, which are measured based on the value delivered to customers. Some of these parts include the resources, structure, leadership, human resources, business process, and strategy among others (Jaleha & Machuki, 2018; Handika &Wibowo, 2018). Productivity, employee turnover, profitability and market share are some of the determinants of an organization’s performance (Glunk & Heijltjes, 2009). Talent Retention and Organizational Performance The notable objective of talent management is not only hiring talent but also ensuring their retention in the organization. Factors upon which the retention rate depends are attractive pay package, job specification, safety and security of the employees, personal development of an employee, recognition and culture of the organization, and the fit between the job and talent. The importance also comes from the definition where talent management is defined as a systematic attraction, identification, development, engagement, retention, and deployment of those individuals who possess a high potential that creates a particular value to an organization (Krishnan and Scullion, 2017). A strong retention strategy becomes a powerful recruitment tool. Retention of key employees is therefore important to the sustainability and survival of any organization either with short or long benefits (Salau, 2022). It is a known fact that retaining your best employees ensures customer satisfaction, increased product sales, satisfied colleagues and reporting staff, effective succession planning and deeply embedded organizational knowledge and learning. The term employee retention is said to be the ability of an organization to retain its employees within the organization in the long run. It can be measured in simple statistics like percentage and considered as the outcome of efforts made by the employer to keep employees within the organization; in this sense, it is considered to be the strategy. It is therefore advisable that every organization should maintain its best performers especially in today’s competitive economic arena where competitors are known to poach employees from each other (Farley, 2015). As organizations continue to pursue high productivity and improved results through talent management, they are taking a holistic approach to talent management. Agrela (2018) emphasized the need to focus on the factors that affect employee retention leading to growth and success of organizations as these employees’ productivity improves due to gaining experience as they have worked for a long time in the organization and are conversant with the organizational culture and processes. Training and Development and Organizational Performance Aswathappa (2018) attempts to draw a distinction among training, education, and development and argues that training is the process of imparting specific skills while education on the other hand is confined to theoretical learning in the classroom. He further defines development as the learning opportunities designed to help employees grow. To ensure a zero-talent outage and to further ensure a planned succession as against a replacement from outside, many organizations now engage in talent development activities that can enhance their organizational reputation as talent hunters (Salau, 2022). Staff development and training activities are designed to help an organization meet its skills requirement and to help its employees realize their maximum potential with the overall aim of implementing its strategy and ensuring the success of the organization (Ashton & Morton, 2015). Talent development can go through several stages, such as developing subordinates, managers, and certification. Each organization in the world has its own talent development policy (Cheloha and Swain, 2005), because there are no common standards which should be applied in all organizations (Lehmann, 2009). One of the main purposes of talent management is to classify employees in categories according to their skills (Thomas, 2009), to determine who are highly qualified and who are the poor performers (Hills, 2009). Upon identifying poor performers, the talent management process must be able to take actions to specify whether the employee is unskilled, which will urge the need to train him (McDonnel et al. 2017), or that poor performers will be identified and then moved to other positions where they would show their inner skills (Blass, 2007). Training is a learning process that involves the acquisition of skills, concepts, rules, or attitudes to increase organizational performance (Blass, 2017). Aswathappa (2018) continues to argue that the organization must offer a wide range of development provision, enabling staff to gain the skills, competences, and experience necessary to contribute to the attainment of individual, team and organizational goals and expectations. Talent Attraction and Organizational Performance Attracting the right talent has become a great challenge for businesses today. According to Storey et al. (2010), both public and business sector organizations are finding it increasingly difficult to attract and keep talented workers, especially younger, highly skilled staff. This is supported by a survey, which was conducted by Deloitte, which found that the ability to attract and retain talent is one of the most critical issues of people management that face organizations today (Lyria, 2014). The attraction of the workforce is an important part of the organization’s performance, and it usually starts by launching a job, and ends with new employment. Talent attraction has become a great challenge for modern organizations. The components of talent attraction are recruitment and selection, employer branding, employee values proposition and employer of choice (Armstrong & Taylor, 2016). THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK Human Capital Theory (Becker 1964) This theory postulates that human capital – the composition of employee skills, knowledge, and abilities – is a central driver of organizational performance. Hills (2009) asserts that human capital is the time, experience, knowledge and abilities of an individual household or a generation, which can be used in the production process. This theory contends that peoples learning capacities are comparable to other natural resources, when effectively exploited the results are profitable to the organization. Therefore, the human capital theory helped to examine how talent management could enhance recruitment processes that are essential to employee performance. The relevance of this theory to talent management is that human capital consists of various components, skills, time, experience and knowledge which are talent embedded in individual employees. Joyce et al. (2007) defines talent as the core competencies and skills embedded in people and are the points of advantage for employee performance. Human Capital theory explains the collective capability, knowledge and skills of the people that are employed by an organization and therefore will be useful in examining how talent is acquired with regards to skills and knowledge and how capability is developed through training and development and its influences on employee performance. Empirical Review Talent management has been studied by various authors but in different aspects and directions. Mahmoud (2019) examined the influence of talent management on performance of employee in public sector institutions of the UAE. The study adopted a descriptive survey research design. The population of the study was 200 public sector employees in UAE. This study adopted a stratified sampling technique to select a sample size of 156 respondents. The questionnaire consisted of open and closed questions, depending on the objectives of the research. The questionnaire consisted of two parts. The initial portion of the questionnaire included queries about common information related to participants’ relationship with the firm. The 2nd part dealt with talent management strategies and aspects of employee performance. The survey is well thought out and structured on a 5-point Likert scale structured questionnaire. Hypothesis was tested with Pearson Product Moment Correlation coefficient. Data was analyzed both for descriptive statistics (frequencies and percentages) and inferential statistics (correlation analysis). Data was presented using tables and figures. The findings revealed a statistically significant relationship between talent acquisition strategy and employee’s performance. The findings also showed that there was a statistically significant relationship between talent development and employee performance. The findings revealed also a statistically significant relationship between retention and employee performance and finally the study revealed that there was a statistically significant relationship between talent management and employee performance. This study concluded that component of talent management had positive influence on performance of public sector employees in UAE. The study recommends that there should be healthy and stress free working environment, career progression opportunity, regular training, tolerance of employees’ innovative ideas and transparent and proper promotion policy for the management of talent in the organization. Masri and Suliman (2019) assessed the relationship between talent management, employee recognition and performance in research institutions. A survey questionnaire was used to collect the primary data of the study on talent management (TM) and employee recognition (ER) on employee performance (EP). The questionnaire was circulated to 180 employees from various positions, educational backgrounds working at the selected research institution in Qatar on a 5-point Likert scale structured questionnaire. Hypothesis was tested with Pearson Product Moment Correlation coefficient and linear regression analysis was used to analyze the data collected. The findings revealed a positive relationship between talent management and employee performance. The study concluded that a strong positive statistically significant relationship exists between talent management and employee performance. The authors advocated that the management should work on creating an ethical work environment by promoting a culture of trust and fairness through an ongoing, open discussion between colleagues and managers in order to reduce work distress and increase the employee engagement that can enhance overall employee performance. Laksono and Mrihrahayu (2021) conducted the impact of employee engagement on talent management and knowledge management on employee performance in the social security administration for employment at the main branch office in Surakarta. In this study, out of 200 employees of the Social Security Administering Body Employment (BPJS) Surakarta, which consists of KLOK Karanganyar, KLOK Sragen, KLOK Wonogiri and KLOK Sukoharjo, the authors used 67 respondents who were taken from 4 KLOK plus 15 Surakarta Office employees in particular on a Likert scale structured questionnaire. Statistical tool used in the survey was path analysis. Findings revealed that the results were the same with those of Irtamieh et al. (2016), showing that talent management has a significant impact on employee performance through employee management. In conclusion, the study noted that employees should be able to better manage their talents and knowledge, either from previous experience or from seminars, training provided by the company and also employees should be able to maintain a good enough performance and be able to improve their optimal performance to contribute to organizational development, especially in BPJS Ketenagakerjaan, Surakarta Main Branch Office. Mohana, Kathari, Rama and Kasa (2021) investigated the impact of talent management on employee job performance. Talent management is a must, irrespective of size, sector and location of the company. An attempt was made to contact the information technology companies in Chennai through emails as majority of information technology companies are located in these areas in South India. In response to this, five companies positively responded and permitted the conduct of the research. As many as 1200 questionnaires were mailed to employees in the selected companies. Out of the received filled-in questionnaires, 222 were with full information in all respects. Hence the sample size was 222 employees. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and Multiple Regression were used to analyze the data collected. Hence, after complying with Reliability and Validity checks using Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA), estimation of overall Model fit was done using structural equation modelling. The study concludes that talent retention, leadership and rewards are impacting significantly on employee job performance of information technology companies in Chennai City. Srihandayani and Kusnendi (2018) conducted research on the effect of talent management and organizational culture on the performance of employees (Study on Employees of Brantas Abipraya Company, Jakarta). Talent management is a complex procedure for the organization but organization needs talented employees to maximize and review their organizational performance. Talent management involves positioning the right people in the right jobs for optimal success of the organization. The aim in this study was to investigate the relationship between talent management and organizational culture on the performance of employees of Brantas Abipraya Company, The method used was descriptive quantitative. Primary and secondary data were used for the study. Thus the data were collected through questionnaire, surveys, interviews and literature review. Data analysis techniques used was descriptive analysis and simple linear regression analysis. This study was carried out in the Brantas Abipraya Company located at Jalan DI Panjaitan Kav 14 Cawang. The target population of the study was 35 managers in the headquarters of Brantas Abipraya Company. The results showed that talent management and organizational culture had significant effect on employee performance. The authors advocated that Strong organizational culture may affect employee performance. The author advocated that a strong organizational culture can encourage the behaviour of its employees and other elements of the company to improve its performance, so as to improve company performance. Hasmin, Jumiaty, Nasriani and Yusriadi (2023) examined talent and knowledge management on employee performance in public organizations. This research was conducted in two public health centers, namely Durikumba Health Center and Lara Health Center, in Karossa District and Central Mamuju Regency. The sampling technique used was total sampling. However, in this study, only 70 out of 74 health workers completed the questionnaire completely at the Durikumba Health Center and 45 out of 53 officers at the Lara Health Center. The total final sample obtained was 115 health workers. The model and research approach used explanatory quantitative by choosing structural equation modeling (SEM) as the basis for statistical analysis to determine the influence and relationship between variables processed using AMOS software. The study’s results found that talent management can encourage knowledge management improvements and improve health workers’ performance at the research sites. Based on the results of research and discussion, it can be concluded that talent management can improve knowledge management and employee performance simultaneously. So, if talent management is carried out properly, it will produce employees who perform well and, on the other hand, can improve knowledge management properly. Faruna, H. A. (2018) examined the impact of talent management on employees’ performance in ceramic firms in Kogi State, Nigeria. The study was anchored on Becker’s 1964 human capital theory. Correlation survey research design was employed for the study. The population of the study was 1058 consisting of employees of the two ceramics firms in Kogi State and 290 were proportionately elected to consist the sample for the study. Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient was used to test the hypotheses. The findings revealed that a significant positive relationship still exist between job satisfaction and talent retention (r = 0.947, p value < 0.05); also, a significant positive relationship exists between career progression and employee commitment (r = 0.974, p-value< 0.05) and yet, a significant positive relationship still exist between training and employees competence (r = 0.963, P – value<0.05). The study concluded that talent management contributes significantly to performance of the employees in ceramic firms in Kogi State. It was recommended that organizations should provide an encouraging wages and promote employees as and at when due to make them linger on to stay with the firm; opportunities should be provided for the employees to advance in their career. Mgbemena, Enetanya, Nsofor and Ogbogu (2022) investigated Talent Management and Organization Performance in Pharmaceutical Companies in Anambra State, Nigeria. The study reviewed relevant conceptual, theoretical and empirical literatures. This study is anchored on Human Capital Theory. Talent retention, training and talent attraction were employed as the explanatory variables while employee performance served as dependent variable. The study adopted survey research design. The population of the study comprised of the staff of the selected pharmaceutical companies in Anambra State, Nigeria. 1800 sample size of 353 respondents was selected for the study using Borg and Gall (1973) formula. Questionnaire was employed as the main instrument of data collection. The data generated were analyzed using frequency, percentage analysis, and multiple regression analysis. The study found that talent retention has a significant influence on employee productivity. Performance management systems have a significant effect on employee productivity. Training and development have a significant influence on employee productivity and talent attraction has a significant effect on employee productivity. The study concluded that talent management has a significant effect on employee productivity. The study therefore recommended that management should establish talent retention strategies and make them known to all employees. Management and employees should be involved in the entire process of performance appraisal which should be made mandatory. To enhance employee productivity, it is imperative that the organization focuses on training and developing programs that are not only essential but enhance employees’ competitiveness. Programs should be designed by both managers and employees. Talent attraction such as competitive salary packages and rewards that keep employees motivated should be established as a policy in every organization. Poonam and Mohsin (2020) examined talent management efficiency in succession planning: a proposed model for pharmaceutical companies. This article provides an insight to pharmaceutical companies about their TM strategies and its impact on their succession planning. But the suggested model has some limitations as the model is not supported by some empirical evidence. The developed model is based on the literature review in the field and there is no empirical study done to support the model. Future research scope is there to test hypothetical model with the help of using statistical tools and techniques after collecting data. Data can be collected from the pharmaceutical companies about their practices and strategies for talent management. The study concluded that the pharmaceutical industries are struggling with talent retention issues; and without retaining the best talent succession planning cannot be designed. Continuous hiring for required leaders will not help in winning the war for talent. Succession planning and management in pharmaceutical industry needs strong TM strategies to be implemented. This model suggests the right strategies for succession planning in pharmaceutical companies with the help of literature review though, but another article can focus on empirical and statistically proven study. Such research would become a guide for pharmaceutical companies to develop their succession plans. Oluwadurotimi and Adedeji (2019) conducted research on Talent Management and Employee Performance in Deposit Money Banks in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. The study objectives investigated the talent management practices adopted by deposit money banks in the study area and examined the effect of talent management on employee performance in deposit money banks. Descriptive statistics and appropriate inferential statistics were employed for the data analysis. The findings revealed that talent strategy is embedded in the overall strategic plan of deposit money bank with mean value of 3.65, right people with right skills are put in the right places have a mean value of 4.10 and also, talent management planning in deposit money bank is a long-term focus has a mean value of 3.81. The hypothesis testing was conducted using Pearson correlation table between talent management and employee performance. It shows that there are positive correlation values (0.618, 0.622, 0.578, 0.672, 0.715, 0.635, 0.568 and 0.608) between talent management and factors that determine employee performance in a deposit money bank. The study concluded that there is a strong relationship between talent management and employee performance in deposit money bank and thus it must be properly managed in order to improve employee’s performance. The study recommended that strategies used in retaining talented employee in deposit money banks must be improved upon and must be a long-term focus of every deposit money bank in the study area. Wandabwa and Makokha (2021) examined effect of Talent Management Practices on Employee Performance in county government of Bungoma. The study was guided by the following objective: to assess the effect of talent career management on employee performance in the county government of Bungoma. The study was anchored on Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Theory, Human Capital Theory and Job embeddedness Theory. The study adopted descriptive research design. The target population of the study comprised management and a supervisory cadre of 136. The study used census technique since the target population was small. Data collection instrument was structured questionnaire. Pilot testing was done to test the validity and reliability of research instrument. Data was analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics and presented in tabular form. Data will be subjected to correlation and Multiple Regression Statistical Methods. From the findings, the study revealed that talent career management was found to a significant positive relationship on employee performance in the county government of Bungoma. The study findings will be useful for human resource management practice, policy formulation and research works. The study findings will help counties in evaluating the importance of talent management on the performance of their employees in terms of quality of work, quantity of work cooperation with other peers, absenteeism and dependability at work. Dim and Udu (2021) assessed talent management and employee commitment in selected pharmaceutical companies in Nigeria. Descriptive survey approach was applied, data were sourced from a five-point Likert scale structured questionnaire. The study was anchored on Becker’s Human Capital Theory of 1964. Population of 1968 represented all the selected pharmaceutical companies used in the study sample of 322 employees derived using Cochran sample size recommendation. Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient was used to test the hypothesis; findings revealed that a significant positive relationship exists between talent retention and employee commitment in the pharmaceutical companies used. Significant positive relationship exists between career advancement and employee commitment in selected pharmaceutical companies used and positive relationship also exists between talent management and employee engagement in selected pharmaceutical companies used in the study. The study concluded that talent management contributes significantly to employee commitment of pharmaceutical companies. Recommendations were made that these pharmaceutical companies should identify and build those qualities that should attract talented employees because in doing so, they will retain them. Pharmaceutical companies should employ people that are fit to develop their career so it will be of advantage to the company. Igomu, Ozah and Ogbu (2022) examined Talent management and employee retention in Federal Medical Centre, Keffi, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. This study adopted survey design with a sample size of 400 employees of the Centre. A five-point Likert-type scale questionnaire was used to elicit responses from them. The questionnaire was mailed to the respondents electronically on Google forms using WhatsApp and email addresses but only 357 usable copies were returned and analyzed using Partial Least Square Structural Equation Model. Findings revealed that talent attraction has positive but insignificant effect on employee retention while talent development has positive and significant effect on employee retention at Federal Medical Centre, Keffi, Nigeria. This study recommended that Federal Medical Centre, Keffi, Nigeria should continue to develop talent of high performers for potential new roles, identify their knowledge gaps, and implement initiatives to enhance the competencies among its employees. This research contributes additional knowledge for human resource managers to identify whether there is an improvement in employee retention when implementing the right talent management practice in the organization. Alsawalhah (2020) studied talent management strategy and its impact on employee’s development: An Empirical Study on Jordanian Pharmaceutical Companies. The study was based on descriptive and analytical approaches. A questionnaire was designed for this study and was distributed to the sample of the community with a total of 280 questionnaires; 239 questionnaires, representing 85%, were returned. The study results show that there is an important role for strategic talent management in employee development in Jordanian pharmaceutical companies. The researchers recommended: developing a compensation system to encourage workers to stay in companies, supporting talented workers, involving them in important company decisions, developing specialized training programs to develop the skills and capabilities of talented workers and developing performance evaluation programs for talented workers. Eny, Budi, Tjipto, Sudarmiatin and Farika (2021) conducted research on talent management and organizational performance: the mediating role of employee engagement. The goal of talent management is to create high performance, sustainable organizations that meet their strategic and operational goals and objectives. Interesting, selecting, engaging, developing, and retaining employees are the top five focuses of talent management. So that companies would gain a competitive advantage, the demand for human resources will continue to encourage talent management. Data were obtained from questionnaires distributed to midwives who work in private hospitals in East Java, Indonesia. Out of 200 questionnaires distributed, 172 were eligible and were distributed to employees in particular on a Likert scale structured questionnaire. The findings of the study showed an indirect relationship; the role of employee engagement as a mediator in the relationship between talent management and organizational performance shows a greater value than the direct relationship between talent management and organizational performance. The study suggested that since the midwife profession is spread throughout Indonesia, it is hoped that this type of research will further expand the reach of the respondents so that more novelties can be found in accordance with the changes and needs of the community. Research Design and Area of the Study This study adopted descriptive survey research design which serves best for this type of research work while the area of study covers pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. The population of this study consists of 1824 employees of the ten pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. The sample size comprises 356 using Borg and Gall (1973) formula. With respect to this research work, the researcher makes use of primary data. The primary sources of data include the questionnaire and the personal interview. Questionnaire was used as the instrument of data collection while section B includes questions on talent management and organizational performance. The researcher used face and content validity. Test-retest and Cronbach’s alpha was used to verify the internal consistency of each construct. The Cronbach’s Alpha results show that talent retention, training and development, talent attraction and organizational performance recorded reliability coefficients of 0.79, 0.74, and 0.71 respectively. Based on the threshold, they are found to be reliable for the study. The analysis of data was performed using SPSS package. This involved descriptive analysis. Data were cleaned before analysis to ensure that they were correctly captured from source documents. Multiple regression analysis was used to assess the effect of talent management and organizational performance. P value was considered significant at level 0.05. Table 1 below shows the population of this study consists of 1824 employees of the ten pharmaceutical companies in the Niger Delta, Nigeria.
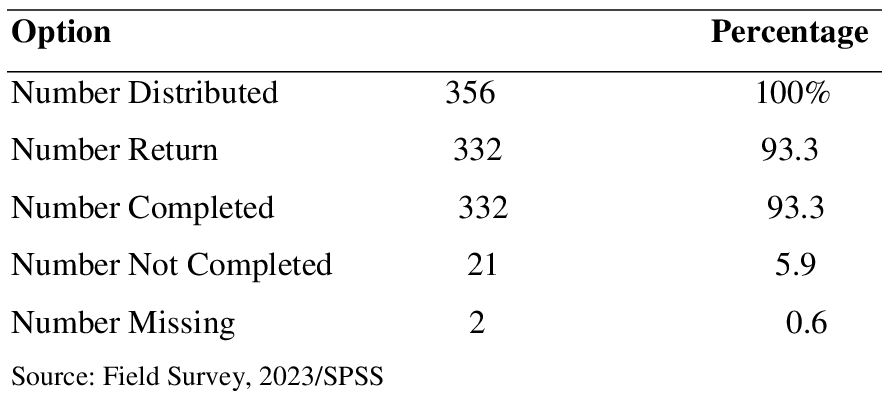
DATA PRESENTATION AND ANALYSIS Administration and Retrieval of Instruments Table 2 below shows the number of questionnaires distributed, the numbers retrieved and the number deemed suitable for the analysis. Note that the copies of the questionnaire not properly filled were not fit for screening requirements and therefore not used for the analysis. Table 2: Questionnaire Distribution and Return
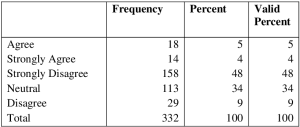
Table 2 reveals that a total of three hundred and fifty six (356) copies of questionnaires were distributed to the respondents, out of which three hundred and thirty two (332) was properly filled and found relevant to the study. 21 copies were not properly filled and 2 got missing. Therefore, the analysis in this section will be based on the three hundred and thirty two relevant copies. RESULTS Presentation of Data relevant to the Research Questions Here, data relevant in answering the research question and testing the hypotheses were presented in tables below. Table 3: Respondents View on Whether Organization Identifies and Prepares Suitable High Potential Employees to Replace Key Players.
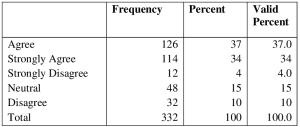
Greater percentage, 37% of respondents, agree that organization identifies and prepares suitable high potential employees to replace key players, 34%strongly agree, 4%are neutral, 15% disagree while 10% of respondents strongly disagree. Table 4: Respondents Opinion on Organization Systematic Succession Plans
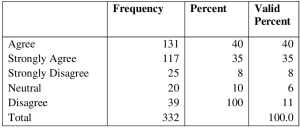
Table 4 reveals that; /35% of the respondent strongly agrees that organization has systematic succession plans, enabling employees to effectively perform roles traditionally reserved for managers 40% agree,8% are neutral, 6 % disagree while 11%of respondents strongly disagree. Table 5: Respondents View on Whether Organization Succession Planning Programs Strongly Influences Staff Retention
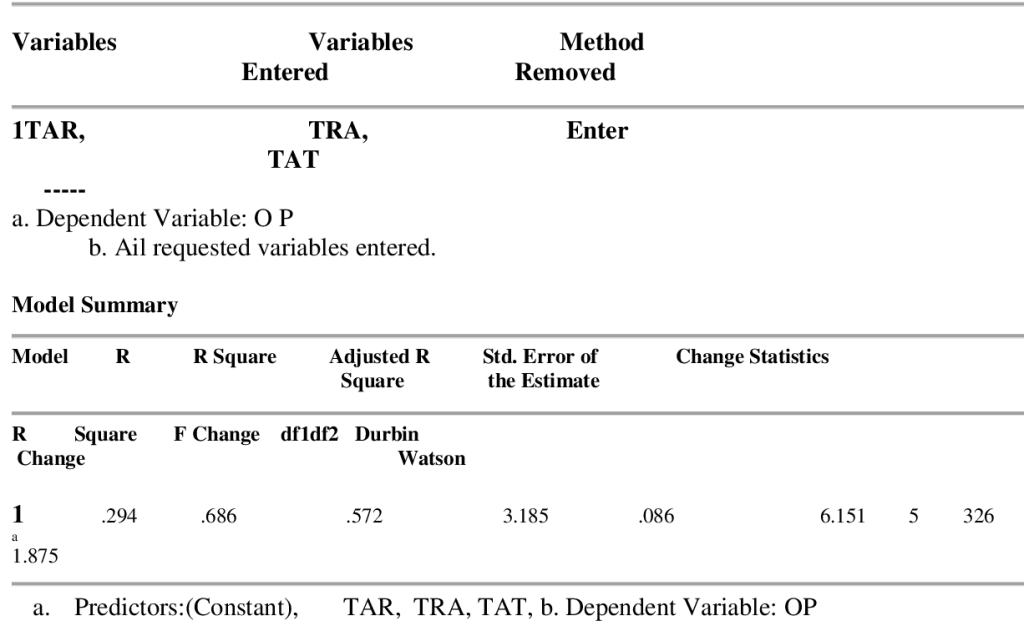
Table 5 shows that 48% of the respondents agree that organization succession planning programs strongly influences staff retention 34% strongly agree, 9 % are neutral, and 5% disagree while 4 % of respondents strongly disagree. Multiple Regression Analysis Multiple regression result was employed to test the effect of independent or explanatory variables on the dependent variables. The result of the multiple regression analysis is presented in the tables below. Table 6: Summary of the Regression Result The result of the multiple regression formulated is presented in the tables below.
Table 6 shows that R2 which measures the strength of the effect of independent variable on the dependent variable have the value of .572. This implies that 69% of the variation in organizational performance is explained by variations in talent retention, training and development, talent attraction. This was supported by adjusted R2 of .086. In order to check for auto correlation in the model, Durbin-Watson statistics was employed. Durbin-Watson statistics of 1.875 in table 6 shows that the variables in the model are not auto correlated and that the model is reliable for predications.
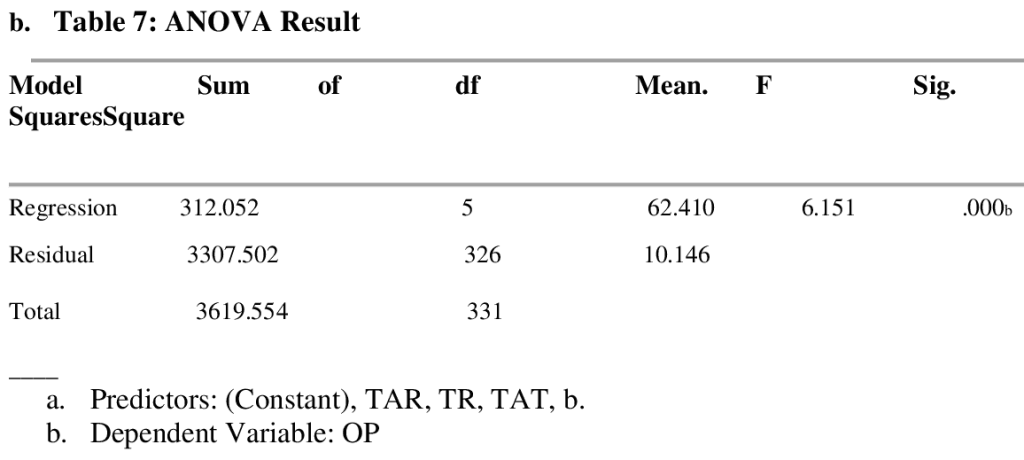
The f-statistics value of 6.151 in table 7 with f-statistics probability of 6.151 shows that the independent variables have significant effect on dependent. This shows that talent retention, training and development, and talent attraction can collectively explain the variations in organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies. Table 8: Coefficients of the Model
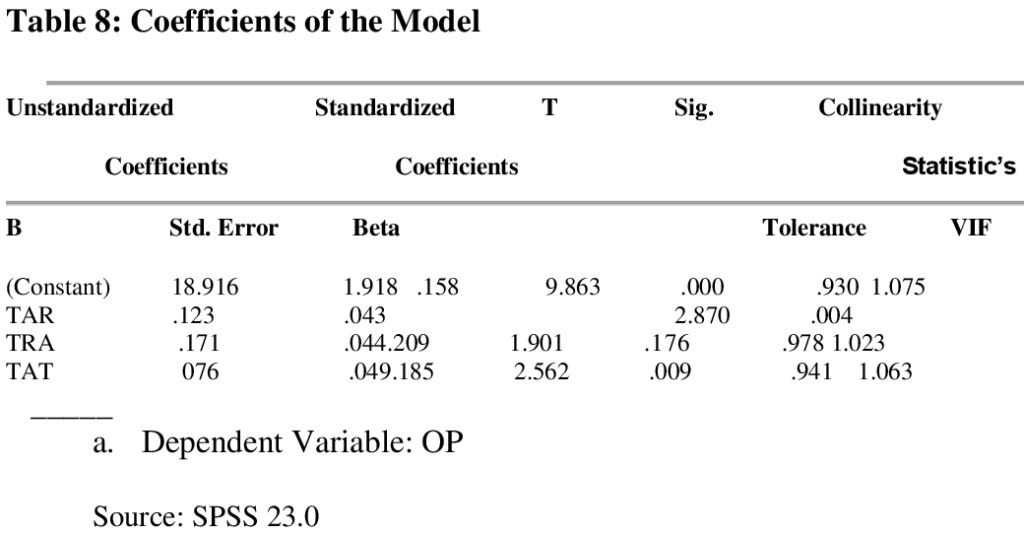
Table 8 shows the coefficient of the individual variables and their probability values. Talent retention has regression coefficient of .123, a probability value of .004. This implies that stress associated with Talent retention has a positive but insignificant effect on employee performance. Furthermore, training has a regression coefficient of .171 with a probability value of .176. This implies that training has a negative and significant effect on employee performance. On a similar note, talent attraction has a coefficient value of .076 and a probability value of .009. This shows that talent attraction has a negative and significant effect on employee performance. Finally, assurance has a coefficient value of .028 and a probability value of .000. This shows that assurance has a negative and significant effect on employee performance. Hypothesis One Ho: Talent retention has no positive significant relationship with organizational performance Ho1: Talent retention has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance In testing this hypothesis, the t-statistics and probability value are used. Talent retention has a statistics of 9.863 and a probability value of .000 which is statistically significant. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypotheses which state that talent retention has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. Hypothesis Two Ho: Training and development has no positive significant relationship with organizational performance Hi: Training and development has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance, training and development has a t-statistics of 3.632 and a probability value of 0.000 which is statistically significant. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypotheses which state that Training has a significant influence on organizational performance. Hypothesis Three Ho: Talent attraction has no positive significant relationship with organizational performance. Hi: Talent attraction has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance Talent attraction has a t-statistics of 2.923 and a probability value of .005 which is statistically significant. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypotheses and conclude that talent attraction has a significant effect on organizational performance DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS The main objective of this study is to examine the effect of talent management and organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation and multiple regression analysis. The result of the multiple analysis shows that talent retention has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. This finding is consistent with that of Agrela (2018) who noted that talent strategies enable an organization to pursue high productivity and improved results through talent management. Agrela (2018) argued that talent strategies enabled organizations to focus on factors that affect employee retention leading to growth and success of organizations as employees’ productivity is enhanced through talent programs within the organizations. This finding agrees with the organizations of future talents which are needed at all organizational levels. Talent retention process is supported by Guthridge, Harttig, Komm and Lawson (2018) who noted that the primary role of talent retention is to enhance easy identification to obtain an optimal talent positioning level that refers to having the correct talent at both the right time and place. This is in line with Aswathappa (2018) argument that training and development improves current or future organizational performance by improving an employee’s ability to perform through learning, usually by changing attitudes or increasing skills and knowledge. This finding is confirmed by Cheboi (2014) argument that employee training generates an improvement in productivity-related benefits for both the organization and the employee. Finally, the study found that talent attraction has a significant effect on organizational performance. This study agrees with the findings of Ballesteros (2018): employer branding includes development of an organization’s image, which is good enough to attract employees. In order to attract the best, organizational branding is a useful strategy; the organizations that manage their corporate brands effectively gain advantage in the highly competitive global market place. Tanuja (2017) noted that top rated companies have one characteristic in common, that is, they give clear and consistent messages about themselves and that translates into a strong pull on talents. Oehley (2017) agrees with the findings that employees measure value proposition based on the challenge the job possess, work environment, training opportunities, flexibility and reputation of the organization. Summary of Findings This study examines the effects of talent management and organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. The study adopted simple percentage analysis and Multiple Regression Analysis in analyzing the data generated. The data analyzed show that:
CONCLUSION This study examines the effects of talent management and organizational performance using pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. The analysis shows that talent retention has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. Training and development have a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. Talent attraction has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance. Therefore, the study concludes that talent management has a positive significant relationship with organizational performance in pharmaceutical companies in Niger Delta, Nigeria. RECOMMENDATIONS Based on the findings of this study, the following recommendations emanated:
REFERENCES Agrela, R. (2018). Retention issues and solutions: tools to ensure University of California becomes an Employer of choice. Journal of Human Resource Management, 4, 765-783. Almutairi Mohammad & Alsawalhah, Ayyoub. (2020). The Impact of Strategies Human Resource Management on Organizational Commitment. (An Applied Study on Employees in Jordanian Islamic Banks). Modern Applied Science, 14(4). Alsawalhah, A.A (2020). Talent Management Strategy and its Impact on Employee’s Development: An Empirical Study on Jordanian Pharmaceutical Companies. Modern Applied Science, 14(5), 1913-1852. Amina, R. M. & Parbudyal, S. (2020). “Outcomes of talent management: the role of perceived equity”. Employee Relations: The International Journal. DOI: 10.1108/ER-04–0153. Armstrong, M., & Taylor, S. (2016). Armstrong’s Handbook of Human Resource. United Kingdom: Kogan Page. Ashton, C. & Morton, L. (2015). Managing talent for competitive advantage. Human Strategic Review, 4(5), 28-31. Ayub, S. Z. (2017). The impact of talent management on employee engagement and retention in achieving organizational performance. Science International, 29(6), 1277-1281. Bersin, J. (2016). Talent Management, What is it, Why Now. Hay Acquisition Company 1, Inc. Blass, E., (2017). Talent Management: Maximizing talent for business performance: Executive Summary. Chartered Management Institute. Cheboi, D. K. (2014). Influence of extrinsic motivation on employee’s productivity in MOI teaching and referral hospital Eldoret, Kenya (Doctoral Dissertation, University of Nairobi). Cheloha, R. and Swain, J., (2005). Talent management system key to effective succession planning. Canadian HR Reporter, 18 (17), 5-7 Deepika, P., & Sampurna, R. (2018). “Talent management and employee engagement – a meta-analysis of their impact on talent retention”, Industrial and Commercial Training, 4, 185-199. Derda D. & Dea Flores D.O.O., (2017). International Experience in Upper Echelon Theory: Literature Review. Business Systems Research, 8(2). Dim, E. M., &Udu, G. O.C. (2021).Talent Management and Employee Commitment in Selected Pharmaceutical Companies in Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) 9, 2279-0845. Eglal Hafez et al., (2017). “An exploratory study on how talent management affects employee retention and job satisfaction for personal administration in AIN Shams University, Egypt”, Journal of Management and Strategy, 1-7. Eny, Y., Budi, E.S., Tjipto, W., Sudarmiatin, & Farika, N. (2021). Talent management and organizational performance: The mediating role of employee engagement. Management Science Letters 11, 2341–2346. Erkut Altindağ et al., (2018). “Effects of talent management components on the employee satisfaction”, Journal of Human Resources Management Research, 1-20. Farley, C. (2015). Human resource role in talent management and driving business results. Employment Relations Today, 32(1), 55-62 Faruna, H. A. (2018). Impact of talent management on employees’ performance in ceramic firms in kogi state. A thesis submitted to the college of management and social sciences, Salem University, Lokoja, Nigeria. In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of master Degree (M.Sc) in Business Administration, Department of Salem University, Lokoja, Nigeria. Glunk, U., & Heijltjes, M. (2009). Performance implications of altering team composition International. Guthridge, M., McPherson, J. R., & Wolf, W. J. (2019). Upgrading talent. The McKinsey Quarterly (1). Hailey, J. (2006). NGO Leadership Development: A Review of Literature. Praxis Paper Handika R.F. & Wibowo A., (2018). Top Management Team Diversity, the Strategic Isomorphism and Firms’ Performance: A Study in the Indonesian Banking Industry. Academy of StrategicManagement Journal, 17(3). Hasmin, T., Jumiaty, N., NasrianiC, & Yusriadi, Y. (2023).Talent and Knowledge Management on Employee Performance in Public Organization. International Journal of Professional Business Review ISSN: 2525 3654. Hayfaa, T. (2021). “Exploring talent management in practice: an Arab country-specific empirical investigation”, Employee Relations: The International Journal, 63-81. Hitu & Satyawan B. (2018). “Impact of talent management practices on employee’s performance in private sector bank”. International Journal of Management, 16-21. Igomu, D.M., Ozah, J. P., &Ogbu, J. O. (2022). Talent management and employee retention in Federal Medical Centre Keffi, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Fuw-International Journal of Management and Social Sciences. ISSN: 2384-6224 (Print), 2635-3539 (Online) Jaleha A.A. & Machuki V.N., (2018). Strategic Leadership and Organizational Performance: A Critical Review of Literature. European Scientific Journal, 14(35), ISSN: 1857 – 7881. Krishnan, T.N. and Scullion, H., (2017). Talent management and dynamic view of talent in small and medium enterprises. Human Resource Management Review, 27(3), 431-441. Laksono, S., & Mrihrahayu, R. (2021). The impact of employee engagement on talent management and Knowledge management on employee performance in the social Security administration for employment at the main branch office Surakarta. International Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting Research (IJEBAR). 5, 2622-4771. Lehmann, S., (2009). Motivating talents in Thai and Malaysian service firms. Human Resource Development International, 12(2), 155-169. Lyria, R. K (2014). Role of talent management on organization performance in companies listed in Nairobi security exchange in Kenya: literature review. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 3(21) 423-441. MacPherson, H., & Mine P. (2004). Assessing Organizational Performance. The World Conservation Union Report. London: Thompson Learning. Mahmoud, K. (2019). The influence of talent management on performance of employee in public sector institutions of the UAE. Public Administration Research, 1927-5188. Masri, N., & Suliman, A. (2019). Talent management, employee recognition and performance in the research institutions. Studies in Business and Economics no. 14(1). McDonnell, A., Collings, D.G., Mellahi, K. and Schuler, R., (2017). Talent management: a systematic review and future prospects. European Journal of International Management, 11(1), 86-128. Mgbemena et al. (2022). Talent Management and Organization Performance in Pharmaceutical Companies in Anambra State, Nigeria. International Journal of Business & Law Research, 10(4), 1-16. Mohana, S., Kathari, S., Rama, M., & Kasa, S. (2021). Impact of Talent Management on Employee Job Performance. In Information Technology (IT) Sector: An Empirical Study Of Chennai City- Palarch’s Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology 18(4), 1-14. Moza Abdallah Soud et al. (2020). Relationship between talent management practices and organizational performance in Islamic banks in Kenya. International Journal of Research – Granthaalayah, 98-114. Munaza, B., (2019). Impact of talent management practices on employee performance: an empirical study among healthcare employees. SEISENSE Journal of Management, 22-32. Nadine, E.I.M, & Abubakr, S. (2019). Talent management, employee recognition and performance in the research institutions. Studies in Economics and Business, 127-140. Oluwadurotimi, A.M., & Adedeji, A.O. (2019). Talent Management and Employee Performance in Deposit Money Banks in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. IJMSSSR volume 1 issue 2. Oluwatobi I. O, & Gabriel, O. A. (2021). Talent management practices and job performance of librarians in university libraries in Nigeria. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, Volume. 47, Issue. 2. Pamela T. Elia et al. (2017). Talent management implications in the Lebanese Banking Industry. Human Resource Management Research, 83-89. Pella, D. A., & Afifahh I., (2017). Talent Management Mengembangkan SDM untuk Mencapai Pertumbuhan dan Kinerja Prima. Jakarta: PT. Gramedia Poonam, J., & Mohsin, S. (2020). Talent management efficiency in succession planning: a proposed model for pharmaceutical companies. International Journal of Management (IJM), 203-213. Richard, O. C., Murthi, B. P. S., & Ismail, K. (2009). The impact of racial diversity on intermediate and long-term performance: The moderating role of environmental context. Strategic ManagementJournal, 28, 1213–1233. Riham Al Aina &Tarik Atan. (2020). The impact of implementing talent management on sustainable organizational performance. Sustainability, 1-21. Salau, N.A, (2022). Effect of Succession Planning on SMEs Performance in Lagos State, Nigeria. Unpublished Ph.D Thesis submitted to the Dept. of Management and Accounting, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomosho, Oyo State. Srihandayani, U., & Kusnendi, K. (2018). Effect of Talent Management and Organizational Culture on the Performance of Employees (Study on Employee Brantas Abipraya Company, Jakarta). Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, volume 117. Storey, D. J., Saridakis, G., Sen-Gupta, S., Edwards, P. K.and Blackburn, R. A. (2010). Linking HR formality with employee job quality: The role of firm and workplace size. Strategy, 23(3), 32-37. Syed Hussain Al-Hussaini et al. (2019). Impact of talent management strategies on employee performance behaviour with the mediating role of talent management outputs. Archives of Business Research, pp. 116-124. Thomas, K., (2009). Talent strategies for innovation. Economist Intelligence Unit Supported by the Government of Ontario, September, pp.1-10. Wandabwa, N.W., & Makokha, E.N. (2021). Effect of Talent Management Practices on Employee Performance in county government of Bungoma. International Journal of Recent Research in Commerce, Economics and Management (IJRRCEM) Vol. 8, Issue 1, pp.121-137. Wickramaaratchi, D.R. & Perera, G.D.N. (2020). The impact of talent management on employee performance: the mediating role of job satisfaction of generation Y management trainees in the selected public banks in Sri Lanka, Sri Lankan Journal of Human Resource Management, 21-36. |
|||||
|